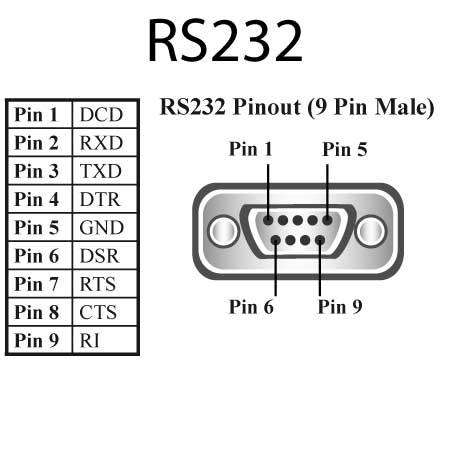
RS-232 Overview:
RS-232 (Recommended Standard 232) is a standard for serial communication between devices using asynchronous communication. It defines the voltage levels and timing of signals used for serial communication over short distances.
Specifications:
- Voltage Levels: Typically uses voltage levels around ±12V for signaling.
- Baud Rate: Common baud rates range from 300 bps to 115200 bps.
- Connectors: Uses DB-9 or DB-25 connectors for serial communication.
- Signal Lines: Includes transmit data, receive data, control signals (such as RTS/CTS), and ground.
-
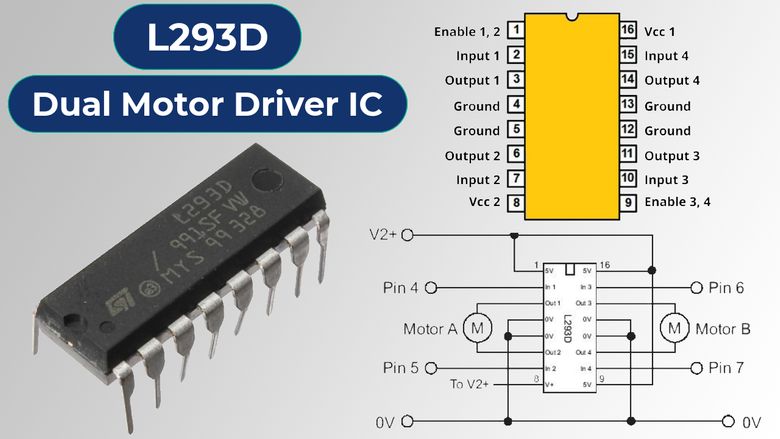
DataSheet
Main Uses:
- Serial Communication: Widely used for communication between computers and peripherals, such as printers, modems, and older serial devices.
- Configuration/Programming: Utilized for configuring and programming devices like routers, switches, and industrial equipment.
- Data Logging: Employed for data logging applications that require serial communication.
- Debugging/Testing: Used for debugging and testing electronic devices and circuits.
- Control Systems: Integrated into control systems for communication between PLCs, sensors, and actuators.
Features:
- Point-to-Point Communication: Typically used for one-to-one communication.
- Simple Interface: Relatively straightforward to implement and understand.
- Reliable Communication: Can provide reliable communication over short distances.
- Half-Duplex Communication: Supports half-duplex communication, where data can be sent or received but not both simultaneously.
- Widely Supported: Despite being an older standard, RS-232 is still commonly found in various industrial and legacy systems.

Application Fields:
- Telecommunications: Used in early modems and communication equipment.
- Industrial Automation: Employed in industrial control systems for monitoring and control.
- Embedded Systems: Integrated into embedded systems for configuration and communication.
- Testing and Measurement: Utilized in testing and measurement equipment for data transfer.
- Legacy Systems: Found in legacy systems that rely on serial communication.
Working Principle:
- RS-232 communication involves the transmission of data in a serial format, typically using start and stop bits to frame each data byte.
- Data is sent using voltage levels to represent binary 1s and 0s.
- Control lines such as RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send) can be used for flow control in RS-232 communication.

Alternative Models:
- RS-485: A more modern standard compared to RS-232, offering better noise immunity and longer communication distances.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus): Commonly used as a replacement for RS-232 in many applications due to its ease of use and higher data transfer rates.
- Bluetooth: Wireless technology that can replace wired RS-232 connections for short-range communication.
- Ethernet: Provides a high-speed alternative for data communication in networking applications compared to RS-232.

When considering alternative models to RS-232 for communication purposes, factors like communication speed, distance requirements, noise immunity, and compatibility with existing systems should be taken into account. Different standards may suit specific applications better based on these factors.