Understanding PMIC (Power Management Integrated Circuit)
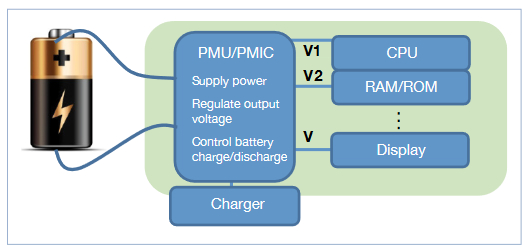
Introduction to PMIC: A Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC) is a type of integrated circuit specially designed to manage power requirements in various electronic devices. PMICs are vital components that ensure efficient power delivery, conversion, and regulation within a system. Here is a detailed explanation of PMIC and how it works:

Key Functions of a PMIC:
-
Power Conversion: PMICs facilitate the conversion of power from one form to another, such as stepping down voltage (buck converter), stepping up voltage (boost converter), or providing both functions (buck-boost converter).
-
Power Regulation: PMICs regulate voltage levels to ensure stable and consistent power supply to different components within an electronic system. They help maintain desired voltages even when power sources fluctuate.
-
Power Sequencing and Monitoring: PMICs manage the sequencing of power rails to ensure that specific components power up and shut down in the correct order. They also monitor power consumption and provide feedback for system optimization.
-
Battery Management: In systems powered by batteries, PMICs manage battery charging/discharging, optimize power usage to extend battery life, and prevent overcharging or over-discharging.
-
Thermal Management: Some PMICs include features to monitor and manage the temperature of the system, helping prevent overheating and ensuring safe operation under varying thermal conditions.
-
Efficiency Optimization: PMICs are designed to improve power efficiency by reducing power losses during conversion, regulation, and distribution, thereby enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the system.
How PMIC Works:
-
Input Power Management:
- Receives power from the input source (battery, AC adapter, USB, etc.).
- Converts the input power to the required voltages using voltage regulators or converters.
-
Voltage Regulation:
- PMICs regulate voltages to ensure that different components receive stable and appropriate power levels.
- Provides multiple output voltages tailored to various parts of the system.
-
Power Sequencing:
- Controls the order in which different power rails are activated to prevent voltage spikes and ensure proper system startup/shutdown sequences.
-
Battery Management:
- Monitors battery status, manages charging/discharging processes, and protects the battery from damage due to overcharging or over-discharging.
-
Monitoring and Control:
- Constantly monitors system parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, and provides feedback for optimization and protection.
- Can communicate with the system processor for dynamic power management based on system requirements.
Applications of PMICs:
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones, tablets, wearables.
- Embedded Systems: IoT devices, industrial automation.
- Computers and Servers: Laptops, desktops, servers.
- Consumer Electronics: TVs, gaming consoles, cameras.
- Automotive Electronics: Infotainment systems, ADAS features.
Conclusion:
Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMICs) play a crucial role in modern electronic devices by efficiently managing power delivery, conversion, regulation, and monitoring. Their functions ensure optimal performance, system reliability, energy efficiency, and protection of components, making them indispensable in a wide range of applications across industries.


